New Release - Schwifty - All About SPNs
These commands were updated Feb 8, 2017 (v0.8.709) to incorporate feedback ❤️
Right, so the first thing you need to know is: I’m not Chrissy. My name’s Drew, and I’m here tell you about an exciting new release of dbatools: schwifty!
In this release we’ve added three new commands to help you manage SPNs for SQL Server Kerberos authentication. If you have a lot of linked servers in your environment, then this is probably a welcome addition to the toolset for you.
These commands leverage SQL Server instance info from commands that already existed in the dbatools code base and active directory PowerShell support to determine required SPNs for all instances on a given computer and whether they’re set or not. If they aren’t, we have commands to not only set the SPNs for you, but also enable constrained delegation to accounts for the SPNs that were just added.
Then
Before these functions were added to dbatools, you had a couple options when it came to checking/adding SPNs:
setspn.exe and ActiveDirectory Users and Computers. setspn.exe is a windows command that you could use to add an SPN to given Active Directory account. And it works great! You do need to know the SPN and account you want to set it for ahead of time; it doesn’t really care about what kind of SPN you’re setting, but it’ll let you set it. You could also use it to check for dupes, list out what SPNs exist for an account… it’s a pretty well documented command. Setting the SPN is only part of what makes SQL Server Kerberos authentication work, though. You still need to set delegation on the account to the services in question. That normally requires you going into the Active Directory Users and Computers application and adding delegation outside of the setspn.exe command prompt. Yuck!
Microsoft Kerberos Configuration Manager for SQL Server. Microsoft does have a tool to help you manage your SPNs for SQL Server too. It’s called Kerberos Configuration Manager for SQL Server and it’s awesome because not only does it tell you what SPNs need set, but it checks to see if they are there. If they aren’t, it’ll try and fix them for you, or generate a .cmd file that you can run on your own. It’s a neat tool that essentially generates SPNs based on best practice straight from Microsoft. While the auto fixing and script generation are neat, the program can be a little slow. Also: up until very recently (2017 Jan 31), it wasn’t compatible with SQL Server 2016. It also doesn’t set delegation for your accounts, either. Less yuck, but still: yuck!
Now
Now we have four new commands to help manage SPNs - Get-DbaSpn, Test-DbaSpn, Set-DbaSpn, and Remove-DbaSpn. Our goal with the new SPN commands was to make them fast, and make them at least as useful as the GUI tool provided by Microsoft, but to allow multi-server administration and automation of setting correct SPNs and enabling constrained delegation. And we’ve done it! These commands are based on guidance from MSDN about setting SQL Server Service Principal names which you can read more about here.
Oh and for the performance minded among you, we’ve built these functions to be super fast; faster than the traditional setspn.exe and Configuration Manager options by quite a bit. While the GUI tool took up to 51 seconds per server, our testing showed the ability to return required SPN info for 9 servers in 9 seconds. That’s 1 server per second, granted, we don’t test for SSAS or SSRS at this time, but we do have it planned, and it’ll still be quick.
Take a look below for a detailed description of the new commands in this release. You can use these new functions by grabbing our latest release (0.8.709).
A couple things to note when using these functions:
You’ll need at least permission to read from your domain’s Active Directory, and in the case of adding SPNs, the ability to modify. That means you’ll need to run the commands as a user with those permissions, or use the -Credential parameters.
Fully explore Get-DbaSpn and Test-DbaSpn commands before moving on to Set-DbaSpn. We also included -WhatIf support in Set-DbaSpn so you can see what SPNs will be added to which accounts before you actually apply them. We’ve done our best to make sure we fully support a variety of different configurations and network names, but you should know what will be applied before you actually do it.
New Commands
- Get-DbaSpn
Returns a list of any service principal names (SPNs) set for a given server or active directory account name
PS C:\github\dbatools> Get-DbaSpn -ComputerName sql2016 | Format-Table Input AccountName ServiceClass Port SPN ----- ----------- ------------ ---- --- sql2016 base\sqlserver MSSQLSvc MSSQLSvc/SQL2016.base.local sql2016 base\sqlserver MSSQLSvc MSSQLSvc/SQL2016.base.local:SQLEXPRESS sql2016 base\sqlserver MSSQLSvc MSSQLSvc/SQL2016.base.local:VWEXT sql2016 base\sqlserver MSSQLSvc 1433 MSSQLSvc/SQL2016.base.local:1433 sql2016 base\sqlserver MSSQLSvc 49903 MSSQLSvc/SQL2016.base.local:49903 sql2016 base\sqlserver MSSQLSvc 49837 MSSQLSvc/SQL2016.base.local:49837 PS C:\github\dbatools> $servers | Get-DbaSpn | Format-Table -AutoSize Input AccountName ServiceClass Port SPN ----- ----------- ------------ ---- --- sql2008 base\sqlserver MSSQLSvc MSSQLSvc/sql2008.base.local sql2008 base\sqlserver MSSQLSvc MSSQLSvc/sql2008.base.local:SQL2K8 sql2008 base\sqlserver MSSQLSvc 1433 MSSQLSvc/sql2008.base.local:1433 sql2008 base\sqlserver MSSQLSvc 49271 MSSQLSvc/sql2008.base.local:49271 sql2012 base\sqlserver MSSQLSvc MSSQLSvc/sql2012.base.local sql2012 base\sqlserver MSSQLSvc 1433 MSSQLSvc/sql2012.base.local:1433 sql2014 base\sqlserver MSSQLSvc MSSQLSvc/sql2014.base.local sql2016 base\sqlserver MSSQLSvc MSSQLSvc/SQL2016.base.local sql2016 base\sqlserver MSSQLSvc MSSQLSvc/SQL2016.base.local:SQLEXPRESS sql2016 base\sqlserver MSSQLSvc MSSQLSvc/SQL2016.base.local:VWEXT sql2016 base\sqlserver MSSQLSvc 1433 MSSQLSvc/SQL2016.base.local:1433 sql2016 base\sqlserver MSSQLSvc 49903 MSSQLSvc/SQL2016.base.local:49903 sql2016 base\sqlserver MSSQLSvc 49837 MSSQLSvc/SQL2016.base.local:49837 sql2016a base\sqlserver MSSQLSvc MSSQLSvc/sql2016a.base.local sql2016a base\sqlserver MSSQLSvc 1433 MSSQLSvc/sql2016a.base.local:1433 sql2016b base\sqlserver MSSQLSvc MSSQLSvc/sql2016b.base.local sql2016b base\sqlserver MSSQLSvc 1433 MSSQLSvc/sql2016b.base.local:1433 sql2016c base\sqlserver MSSQLSvc MSSQLSvc/sql2016c.base.local sql2016c base\sqlserver MSSQLSvc 1433 MSSQLSvc/sql2016c.base.local:1433 sqlcluster base\sqlserver MSSQLSvc MSSQLSvc/sqlcluster.base.local sqlcluster base\sqlserver MSSQLSvc 1433 MSSQLSvc/sqlcluster.base.local:1433 PS C:\github\dbatools> _
- Test-DbaSpn
Returns of listing of “required” SPNs for a given computer’s instance of SQL Server. The cmdlet will discover all instances of SQL Server on a given computer name. For each instance found, the cmdlet will generate a list of required SPNs based on active TCP/IP ports. The cmdlet will also warn you if an instance is using dynamic ports. Each returned SPN object will also specify if the SPN is currently set or not.
PS C:\github\dbatools> Test-DbaSpn -ComputerName sql2005 | Format-Table ComputerName InstanceName SqlProduct TcpEnabled DynamicPort RequiredSPN IsSet Cluster IsOnlineFail DomainPort Warning Error ------------ ------------ ---------- ---------- ----------- ----------- ----- ------- ------------ ---------- ------- ----- sql2005.base.local MSSQLSERVER SQL Server 2005 Enterprise Edition False False MSSQLSVC/sql2005.base.local False False False None sql2005.base.local MSSQLSERVER SQL Server 2005 Enterprise Edition False False MSSQLSVC/sql2005.base.local:1433 False False False 1433 None sql2005.base.local BASE\sqlserver False False MSSQLSVC/sql2005.base.local False False False None sql2005.base.local BASE\sqlserver False False MSSQLSVC/sql2005.base.local:1433 False False False 1433 None sql2005.base.local msdbs-AllowedDelegateto False False msdbs-AllowedDelegateto False False False None sql2005.base.local msdbs-AllowedDelegateto False False msdbs-AllowedDelegateto False False False None
You can even check your entire estate in just one line. Here, you can see us testing several instances in our lab.
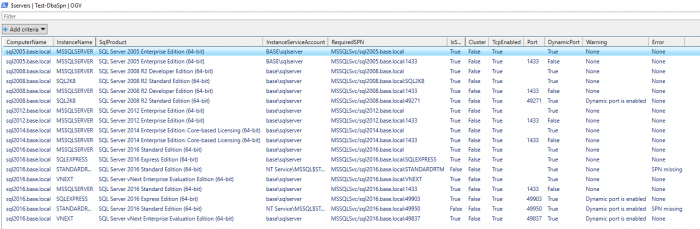
Or use Test to help easily Set all required SPNs
PS C:\github\dbatools> Test-DbaSpn -ComputerName sql2005 | Where-object { !..IsSet -eq $false }
ComputerName : sql2005.base.local
InstanceName : MSSQLSERVER
SqlProduct : SQL Server 2005 Enterprise Edition (64-bit)
TcpEnabled : False
RequiredSPN : MSSQLSVC/sql2005.base.local
IsSet : False
Cluster : False
TcpEnabled : True
DynamicPort : False
Warning : None
Error : SPN missing
ComputerName : sql2005.base.local
InstanceName : MSSQLSERVER
SqlProduct : SQL Server 2005 Enterprise Edition (64-bit)
InstanceServiceAccount : BASE\sqlserver
RequiredSPN : MSSQLSVC/sql2005.base.local:1433
IsSet : False
Cluster : False
TcpEnabled : True
DynamicPort : False
Warning : None
Error : SPN missing
PS C:\github\dbatools> Test-DbaSpn -ComputerName sql2005 | Where-object { !..IsSet -eq $false } | Set-DbaSpn | Format-Table
Name ServiceAccountProperty IsSet Notes
---- ---------------------- ----- -----
MSSQLSvc/sql2005.base.local BASE\sqlserver servicePrincipalName True Successfully added SPN
MSSQLSvc/sql2005.base.local:1433 BASE\sqlserver servicePrincipalName True Successfully added SPN
MSSQLSvc/sql2005.base.local BASE\sqlserver msdbs-AllowedToDelegateTo True Successfully added constrained delegation
MSSQLSvc/sql2005.base.local:1433 BASE\sqlserver msdbs-AllowedToDelegateTo True Successfully added constrained delegation
PS C:\github\dbatools> Test-DbaSpn -ComputerName sql2005 | Where-object { !..IsSet -eq $false }
PS C:\github\dbatools> _
- Set-DbaSpn
Connects to Active Directory and sets a given SPN to a given account. Will also set constrained delegation to the account to the recently added SPN.
PS C:\github\dbatools> Set-DbaSpn -SPN MSSQLSvc/sql2005.base.local:1433 -ServiceAccount base\sqlserver | Format-Table Name ServiceAccount Property IsSet Notes ---- -------------- -------- ----- ----- MSSQLSvc/sql2005.base.local:1433 base\sqlserver servicePrincipalName True Successfully added SPN MSSQLSvc/sql2005.base.local:1433 base\sqlserver msdbs-AllowedToDelegateTo True Successfully added constrained delegation PS C:\github\dbatools> _
Both Set and Remove fully support -WhatIf
PS C:\github\dbatools> Test-DbaSpn -ComputerName sql2005 | Where-object { !..IsSet -eq $false } | Set-DbaSpn -WhatIf
What If: Performing the operation 'Adding SPN to service account' on target 'MSSQLSvc/sql2005.base.local'.
What If: Performing the operation 'Adding constrained delegation to service account' on target 'MSSQLSvc/sql2005.base.local'.
What If: Performing the operation 'Adding SPN to service account' on target 'MSSQLSvc/sql2005.base.local:1433'.
What If: Performing the operation 'Adding constrained delegation to service account for SPN' on target 'MSSQLSvc/sql2005.base.local:1433'.
- Remove-DbaSpn
Connects to Active Directory and removes a given SPN to a given account. Will also remove the associated constrained delegation.
The following screenshot shows a way to easily remove SPNS of decommissioned servers.
PS C:\github\dbatools> Remove-DbaSpn -SPN MSSQLSvc/sql2014:1433 -ServiceAccount base\sqlserver | Format-Table Name ServiceAccount Property IsSet Notes ---- -------------- -------- ----- ----- MSSQLSvc/sql2014:1433 base\sqlserver servicePrincipalName False Successfully removed SPN MSSQLSvc/sql2014:1433 base\sqlserver msdbs-AllowedToDelegateTo False Successfully removed delegation PS C:\github\dbatools> Get-DbaSpn -ComputerName sql2005 | Remove-DbaSpn | Format-Table Name ServiceAccount Property IsSet Notes ---- -------------- -------- ----- ----- MSSQLSvc/sql2005.base.local base\sqlserver servicePrincipalName False Successfully removed SPN MSSQLSvc/sql2005.base.local base\sqlserver msdbs-AllowedToDelegateTo False Successfully removed delegation MSSQLSvc/sql2005.base.local:1433 base\sqlserver servicePrincipalName False Successfully removed SPN MSSQLSvc/sql2005.base.local:1433 base\sqlserver msdbs-AllowedToDelegateTo False Successfully removed delegation PS C:\github\dbatools> _
Related Commands
We also have a few other commands that can help you deal with SPNs.
Repair-DbaInstanceName and Repair-DbaServerName
When a SQL Server’s host OS is renamed, the SQL Server should be as well. This helps with Availability Groups and Kerberos. Repair-DbaInstanceName helps determine if your OS and SQL Server names match, and thus, if a rename is required. If a rename is required, run Repair-DbaServerName.
This command returns the transport protocol and authentication scheme of the connection. This is useful to determine if your connection is using Kerberos. By default, the ConnectName, ServerName, Transport and AuthScheme of the current connection will be returned.
Coming Soon
These commands are just the start of our support for SPNs. Right now, they’re just focused on SQL-related services on your computers. In the future, we’re going to extend these scripts to look at ALL services on your computers and tie them back to service accounts and SPNs. This includes SSAS, SSIS, and SSRS SPN support. We’re also going to keep looking at the commands and adding support for anything we didn’t think of when we released, which is why it’s important that you give us feedback (more on that below).
Thanks for reading, and I hope you enjoy these new commands! If you have any issues or questions about their use, feel free to drop by our Slack channel, #dbatools, and let us know. We’d love to hear from you!
- Drew
 dbatools
dbatools